Uji Matcha
Par Premium Health Japon


Dans un monde de mélanges, nous nous démarquons. Découvrez la pureté d'un matcha d'origine unique et d'un seul cultivar
Accessoires pour le thé Matcha
Produits par catégorie

Fouet en bambou Takayama Chasen de qualité supérieure fabriqué à la main

Fouet à Matcha fabriqué à la main, 100 dents

Ensemble de fouet à matcha ultime – Outils à thé traditionnels en bambou

Pelle en bambou Chashaku de qualité supérieure fabriquée à la main

Support pour fouet à matcha en céramique noire fabriqué à la main (fabriqué au Japon)
Certifié biologique
Japon Agriculture

Matcha Uji certifié

Nom commercial : Premium Health Japan Co. Ltd.
La meilleure poudre de Matcha du Japon
Bienvenue chez Premium Health Japan, vos spécialistes de l'authentique matcha Uji . Basés au Japon avec une équipe bilingue , nous connectons les fermes de thé traditionnelles aux clients internationaux, en proposant des accessoires exclusifs pour le matcha et le thé Uji.
Que vous souhaitiez déguster du matcha de haute qualité ou lancer votre propre marque, nous vous offrons un accès privilégié aux meilleures plantations de thé du Japon .
CE QUE NOS CLIENTS DISENT DE NOTRE MATCHA
Oh mon Dieu(atcha)G !!!
C'est le meilleur matcha que j'ai jamais goûté. Chaud ou froid, il a une saveur forte et onctueuse, une consistance crémeuse, la plus belle nuance de vert vif, et me donne beaucoup de tonus sans nervosité. Je ne peux pas boire ce que j'utilisais avant de découvrir cette marque. Ils font le matcha à la perfection. J'adore. Je le pense. Buvez-le.
Super!
Raffiné, doux et de grande qualité ! La meilleure poudre de matcha que j'ai jamais eue.
Umami !!
C'est un matcha délicieux
Excellence
L’excellence dans un monde de standards inférieurs ; l’authenticité dans un monde de duplicité ; la cohérence dans un monde incohérent !
Excellente qualité !
Un Matcha d'excellente qualité avec une expédition rapide et un excellent service client.
Merveilleux
Ce matcha est vibrant et onctueux avec un arôme doux et terreux. C'est vraiment merveilleux.
Beau
L'un des meilleurs Matcha que j'ai jamais goûté. Vraiment frais et beau.
Incroyable!
Super ! J'adore ce matcha. J'en ai acheté environ 6 jusqu'à présent et je n'irai nulle part ailleurs. La qualité et le goût sont incroyables !!!
Riche et savoureux !
L’arôme de cerise m’a accueillie alors que je me préparais à préparer un bol de matcha. Il était légèrement et agréablement plus prononcé lorsque j’ai versé un peu d’eau chaude sur la poudre tamisée pour créer une pâte. Lorsque j’ai versé le reste de l’eau et que j’ai fouetté, j’ai également senti une légère odeur de chocolat. Je le prépare comme de l’usucha, plus pour pouvoir passer plus de temps (et plus de gorgées !) à savourer le matcha qu’autre chose. C’est merveilleux — plein d’umami, de saveurs complexes et une sensation en bouche riche !
Qu’est-ce que l’Uji Matcha ?
Uji Matcha est un thé vert de qualité supérieure exclusivement cultivé et transformé à Kyoto, au Japon . Il est connu pour sa saveur riche, ses couleurs vives et ses méthodes de production de haute qualité.
Uji Matcha a été certifié authentique par l' Office japonais des brevets et adhère à des normes strictes de culture et de transformation. Sa saveur unique vient des conditions climatiques et pédologiques de Kyoto.
Uji Matcha est traité selon des méthodes traditionnelles, qui aident à préserver son goût riche, sa couleur vibrante et sa qualité supérieure.

Comment préparer le thé Matcha parfait
Il suffit d'ajouter une petite quantité d'eau à température ambiante à votre poudre de matcha et de faire une pâte.
Ensuite, ajoutez de l'eau chaude, mais assurez-vous qu'elle ne bouille pas. Elle doit être à 75 à 80 degrés Celsius. Plus chaude et vous rendrez votre matcha amer.
Fouettez en motifs en "W" et en "M" avec un chasen jusqu'à ce qu'il devienne mousseux. Cela demande de l'entraînement, alors ne soyez pas déçu si ce n'est pas parfait dès le premier essai !
À propos de nous
Premium Health Japan a été fondée par Luke, un ancien entraîneur de boxe australien et expert en fitness qui vit désormais au Japon. Sa quête pour comprendre les bienfaits du thé vert sur la santé pendant la lutte contre le cancer de sa défunte mère l'a conduit au matcha.
Notre matcha est élaboré selon l'approche pratique de Luke, de la ferme au paquet, ce qui garantit une pureté et une qualité inégalées . Notre marque est un engagement en faveur d'un mode de vie authentique et sain ancré dans le riche héritage du matcha.

Notre fondateur - Luc

Une de nos plantations de thé à Kyoto avant la récolte

Notre maître du thé - Kimiko

Notre matcha étant soigneusement pesé et emballé

Nous effectuons des inspections régulières des installations


Premières feuilles de matcha printanières

Les feuilles de Matcha sont tamisées pour un contrôle de qualité avant d'être traitées

Les plants de thé Matcha sont hors saison de récolte dans la ville d'Uji

Notre fondateur - Luc

Une de nos plantations de thé à Kyoto avant la récolte

Notre maître du thé - Kimiko

Notre matcha étant soigneusement pesé et emballé

Nous effectuons des inspections régulières des installations


Premières feuilles de matcha printanières

Les feuilles de Matcha sont tamisées pour un contrôle de qualité avant d'être traitées

Les plants de thé Matcha sont hors saison de récolte dans la ville d'Uji
Rejoignez la Communauté du Matcha Uji
FAQ
Le matcha, en particulier la meilleure poudre de thé vert matcha, est réputé pour ses nombreux bienfaits pour la santé. Il regorge d' antioxydants , en particulier de catéchines , connues pour leurs propriétés anticancéreuses. Le thé vert Matcha améliore également le calme, stimule la mémoire et la concentration, augmente les niveaux d'énergie et brûle des calories. Sa forte teneur en chlorophylle en fait un puissant détoxifiant, et la présence de L-Théanine favorise la relaxation. La consommation régulière de matcha de haute qualité, comme la poudre de matcha la plus savoureuse, peut améliorer la santé cardiaque et aider à la gestion du poids.
En savoir plus sur les bienfaits du matcha pour la santé ici .
La poudre de thé vert matcha japonais est profondément ancrée dans la culture japonaise, principalement pour ses bienfaits pour la santé et son importance cérémonielle . Les Japonais boivent du matcha depuis des siècles, l'appréciant pour sa capacité à stimuler la vigilance mentale et le calme, grâce à la combinaison unique de caféine et de L-théanine . La meilleure poudre de thé matcha est également un incontournable des cérémonies traditionnelles du thé japonaises, reflétant une longue tradition de pleine conscience et d'hospitalité.
Le matcha, en particulier le matcha de haute qualité comme la meilleure poudre de matcha, est souvent considéré comme supérieur au thé vert ordinaire. En effet, le matcha utilise toute la feuille de thé, fournissant ainsi une source de nutriments plus concentrée . Les qualités de Matcha sont importantes ici ; des qualités plus élevées signifient une meilleure qualité et plus de bienfaits pour la santé. Le matcha contient plus d'antioxydants, en particulier de catéchines, que le thé vert, offrant de plus grands bienfaits pour la santé tels qu'une amélioration du métabolisme, une détoxification et une vigilance mentale.
Apprenez-en davantage sur les différences entre le matcha et le thé vert ici .
Le matcha, en particulier la poudre de matcha la plus savoureuse, est une alternative plus saine au café. Alors que les deux fournissent un regain de caféine, le matcha libère lentement de la caféine , assurant un flux constant d'énergie sans la nervosité ou les accidents associés au café. La poudre de matcha japonais est également riche en L-théanine , qui favorise la relaxation ainsi que la vigilance. De plus, le matcha est bon pour la santé en raison de ses propriétés antioxydantes, qui contribuent à la santé cardiaque et à la perte de poids, des bienfaits généralement non associés au café.
Apprenez-en davantage sur le matcha et le café ici .
Oui, il est généralement sécuritaire de boire du matcha, comme la meilleure poudre de thé vert matcha, tous les jours. La consommation régulière de matcha peut être bénéfique en raison de sa teneur élevée en antioxydants , en particulier en EGCG, qui favorise la santé cardiaque et la gestion du poids. Cependant, il est important de choisir des qualités de matcha de haute qualité pour éviter les contaminants et garantir que vous bénéficiez de tous les bienfaits pour la santé. Comme pour tout produit contenant de la caféine, la modération est la clé et il est conseillé de surveiller la réponse de votre corps à la consommation quotidienne de matcha.
Votre guide 2024 des meilleurs thés verts en vrac
Découvrez les meilleurs thés verts en vrac biologiques de 2024 avec notre guide organisé. Découvrez les riches saveurs, les bienfaits pour la santé et la signification culturelle de thés soigneusement...
Introduction au meilleur thé vert en feuilles
Lorsqu’il s’agit de savourer une tasse de thé, la qualité de la feuille compte autant que le rituel de son infusion. Parmi la myriade de variétés de thé, le thé vert occupe une place particulière pour ses saveurs délicates, ses bienfaits pour la santé et le savoir-faire derrière sa production. Ce guide vous fera découvrir le monde de meilleur thé vert en feuilles , explorant non seulement les saveurs mais aussi la culture, les bienfaits pour la santé et les nuances qui rendent chaque feuille unique.
💡 Saviez-vous que le thé vert est consommé depuis des milliers d'années et qu'il était à l'origine utilisé comme boisson médicinale dans la Chine ancienne ?
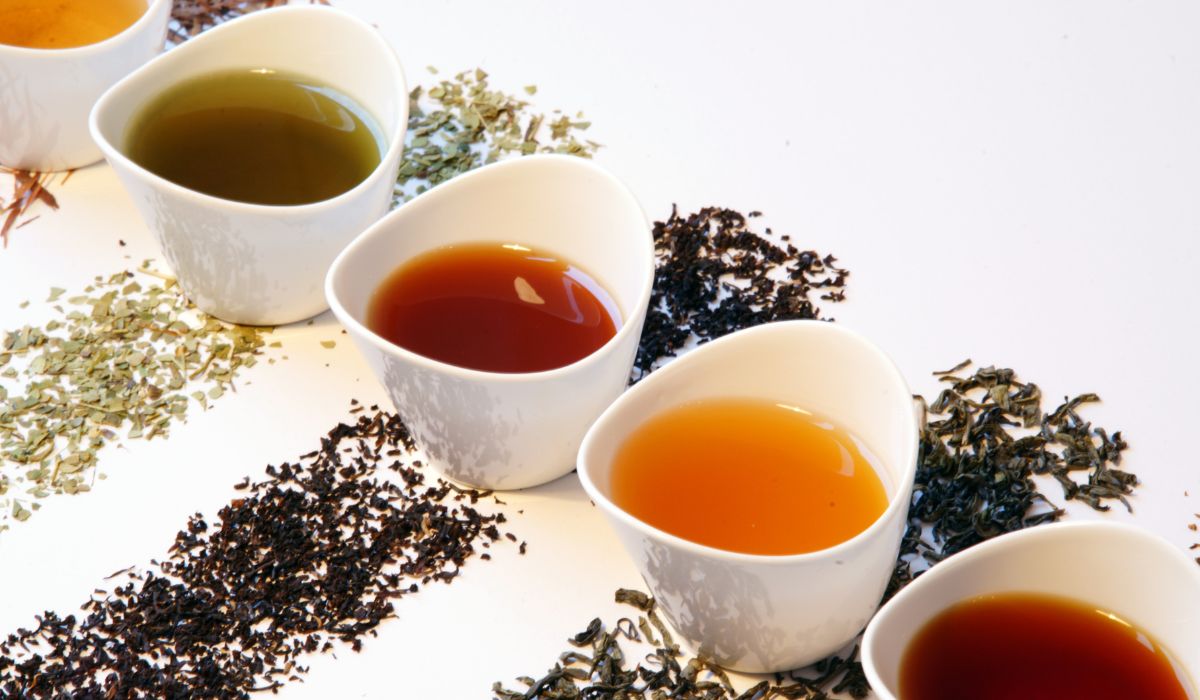
Principaux types de thé (aperçu)
Le thé peut être largement classé en plusieurs types en fonction du traitement des feuilles de la plante Camellia sinensis. Alors que thé noir , thé oolong , et thé blanc ont un charme et des avantages uniques, thé vert et thé aux herbes sont souvent célébrés pour leurs propriétés bénéfiques pour la santé.
Thé vert : Connu pour sa saveur fraîche et délicate, le thé vert subit une oxydation minime lors de sa transformation. Cela préserve sa couleur verte et son profil riche en antioxydants, ce qui en fait un favori parmi amateurs de thé .
Thé noir : Plus oxydé que le thé vert, le thé noir offre une saveur robuste et une teneur plus élevée en caféine. Il se déguste chaud et tel thé glacé , ce qui le rend polyvalent en toute saison.
Thé Oolong : Le thé Oolong est partiellement oxydé, offrant une complexité de saveur qui se situe quelque part entre le thé vert et le thé noir. Son traitement unique donne lieu à des saveurs diverses, allant du sucré et floral au riche et grillé.
Thé blanc : Le moins transformé de tous les thés, le thé blanc est apprécié pour sa subtilité, sa douceur naturelle et son élégance. C'est saveurs douces en font un choix sophistiqué pour les amateurs de thé.
Tisane : Bien qu'elles ne soient pas fabriquées à partir de la plante Camellia sinensis, les tisanes (comme yerba maté et Menthe marocaine ) offrent une alternative sans caféine aux nombreux bienfaits pour la santé.

💡 La saveur unique du thé Oolong résulte d'un processus spécial qui implique le séchage au soleil et l'oxydation avant de friser et de tordre les feuilles.
Le monde du thé vert
Le monde du thé vert est vaste, chaque variété offrant un profil gustatif unique et un ensemble de bienfaits. Des notes herbacées et sucrées de Sencha jusqu'aux profondeurs de noisette de Dragon bien thé, les variétés de thé vert sont aussi diverses que les régions dont elles sont originaires.
-
Thés verts japonais : Le Japon est réputé pour ses thés verts, avec Sencha étant le plus populaire. Cependant, pour ceux qui recherchent le summum de la saveur et de la qualité, Gyokuro se démarque. Le Gyokuro est ombragé avant la récolte, ce qui augmente sa teneur en chlorophylle et lui donne une riche saveur umami.
-
Thés verts chinois : La Chine produit une large gamme de thés verts, dont Chun Mee , connu pour sa douceur semblable à celle d'une prune et sa finale douce. Dragon bien Le thé (Longjing), avec ses feuilles plates distinctives et sa couleur jade, offre une saveur douce et sucrée très recherchée.
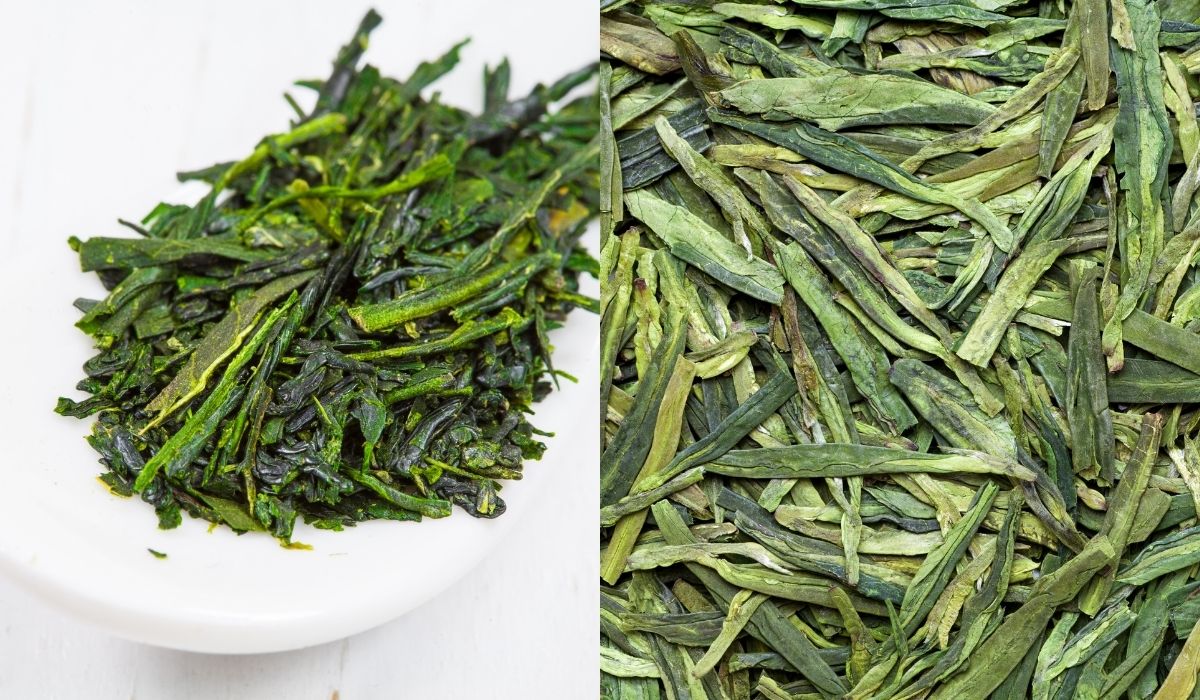

Thé vert bio : Opter pour thé bio c'est choisir des feuilles cultivées sans produits chimiques industriels, garantissant une tasse pure et naturelle. Thé vert bio soutient un mode de vie sain et promeut des pratiques agricoles durables.
Thés verts en feuilles premium : Le terme « premium » est souvent associé aux thés cueillis à la main pendant la période optimale. saison des récoltes , assurant la la plus haute qualité et la saveur. Ces thés, dont des variétés rares et d'origine unique, offrent un tasse corsée c'est à la fois un luxe et une expérience sensorielle.
💡 Le thé Gyokuro est ombragé pendant environ trois semaines avant la récolte, ce qui contribue à sa saveur unique et à sa teneur en caféine plus élevée que les autres thés verts.
Bienfaits du thé vert pour la santé
Le thé vert n’est pas seulement une boisson ; c'est une riche source d'antioxydants et de composés qui affectent profondément votre santé. Voici comment l’incorporation du thé vert à votre routine quotidienne peut vous être bénéfique :
- Perte de poids : Il a été démontré que le thé vert stimule le métabolisme et augmente la combustion des graisses à court terme, ce qui en fait un allié précieux dans la gestion du poids.
- Renforcement du système immunitaire : Les antioxydants contenus dans le thé vert, en particulier la vitamine C et l'acide ascorbique, peuvent aider à renforcer votre système immunitaire, vous rendant ainsi mieux équipé pour combattre les maladies.
- Fonction cérébrale : La consommation régulière de thé vert peut améliorer la fonction cérébrale, améliorant ainsi la mémoire, les performances cognitives et même l'humeur.
- Régulation de la glycémie : Le thé vert peut aider à réguler les niveaux de glucose, réduisant ainsi le risque de pics d'insuline et de diabète.
- Bonne santé et mode de vie sain : Au-delà de ces bienfaits spécifiques, le thé vert soutient un mode de vie sain, contribuant à la santé cardiaque, réduisant le risque de cancer et favorisant la longévité.
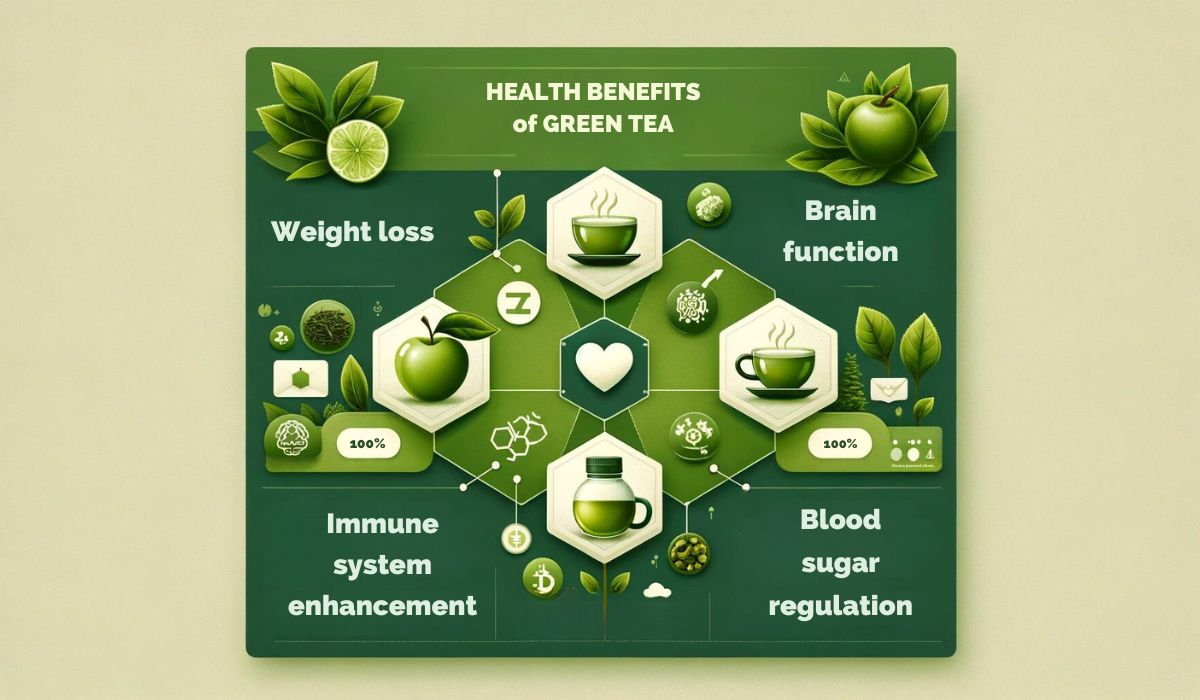
💡 Saviez-vous que le thé vert contient une catéchine appelée EGCG (Epigallocatéchine Gallate), connue pour ses propriétés anticancéreuses ?
Préparer la tasse parfaite
L’art de préparer le thé vert est aussi important que la feuille elle-même. Voici comment vous assurer de tirer le meilleur parti de votre thé vert en feuilles :
- Feuilles en vrac ou sachets de thé : Opter pour du thé en feuilles plutôt que des sachets de thé standard peut améliorer considérablement votre expérience de consommation de thé. Les feuilles lâches permettent une expansion plus complète pendant le trempage, ce qui donne une saveur plus complexe et nuancée.
- Température de l'eau et temps d'infusion : La température idéale de l'eau pour le thé vert se situe entre 150°F et 180°F. L'eau bouillante peut brûler les feuilles, entraînant un goût amer. Le temps d'infusion doit être compris entre 2 et 3 minutes pour un équilibre parfait des saveurs.
- Accessoires pour le thé : Une presse française ou une infusion de thé dédiée permet une meilleure circulation de l'eau autour des feuilles, extrayant un maximum de saveur. La qualité de l’eau peut également avoir un impact sur le goût, c’est pourquoi l’eau filtrée ou de source est recommandée.
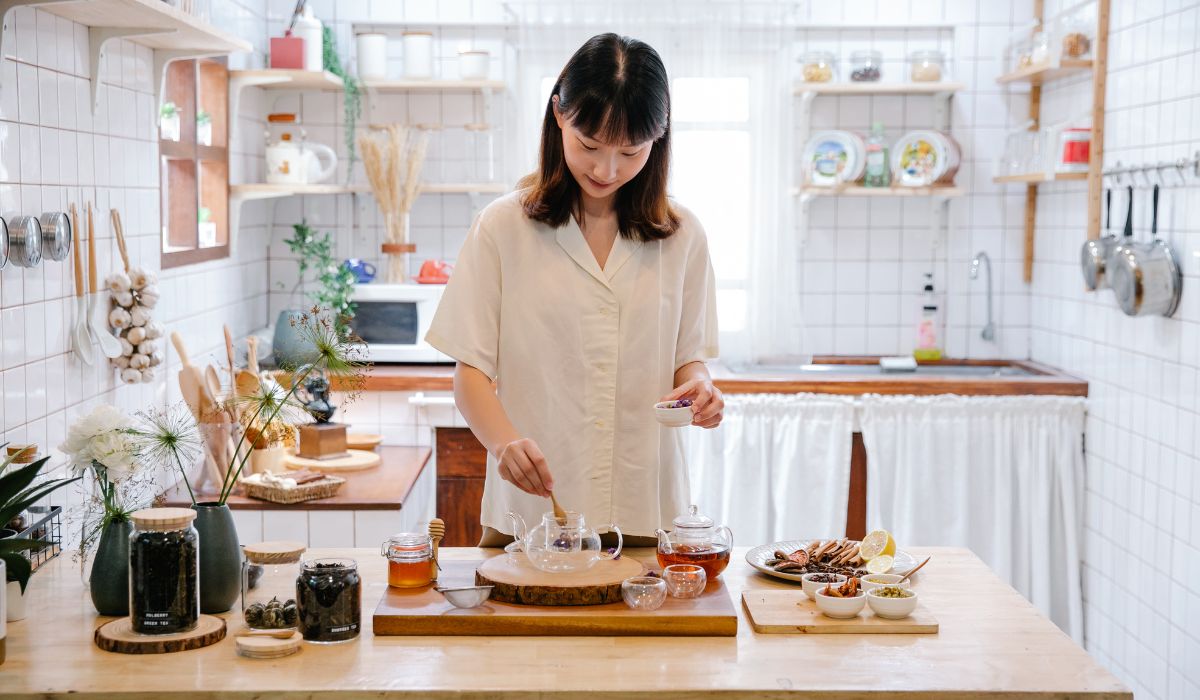

💡 Le terme « trempage » désigne le processus de trempage des feuilles de thé dans l'eau pour en extraire leurs arômes et leurs nutriments, une étape cruciale dans l'infusion du thé.
Culture et consommation du thé
Le thé est plus qu’une boisson ; c'est une expérience culturelle qui varie grandement d'une région à l'autre. Voici un aperçu de la culture du thé et de la manière dont elle façonne notre consommation :
- Amateurs et passionnés de thé : Pour beaucoup, le thé est une passion. Les communautés et forums dédiés au thé permettent aux passionnés de partager leur amour pour les thés rares, les techniques de brassage et les derniers accessoires pour le thé.
- Expérience de consommation de thé : L'expérience de boire du thé peut être profondément personnelle. Certains préfèrent la chaleur apaisante de thés chauds , tandis que d'autres apprécient la vivacité rafraîchissante des thé glacé . L'heure de la journée, l'humeur et même la météo peuvent influencer le choix.
- Cadeaux et échantillons de thé : Le thé est un cadeau attentionné, offrant un avant-goût de différentes cultures et saveurs. Les échantillonneurs de thé sont particulièrement populaires pendant la saison des fêtes , offrant une expérience organisée de thés haut de gamme et rares.
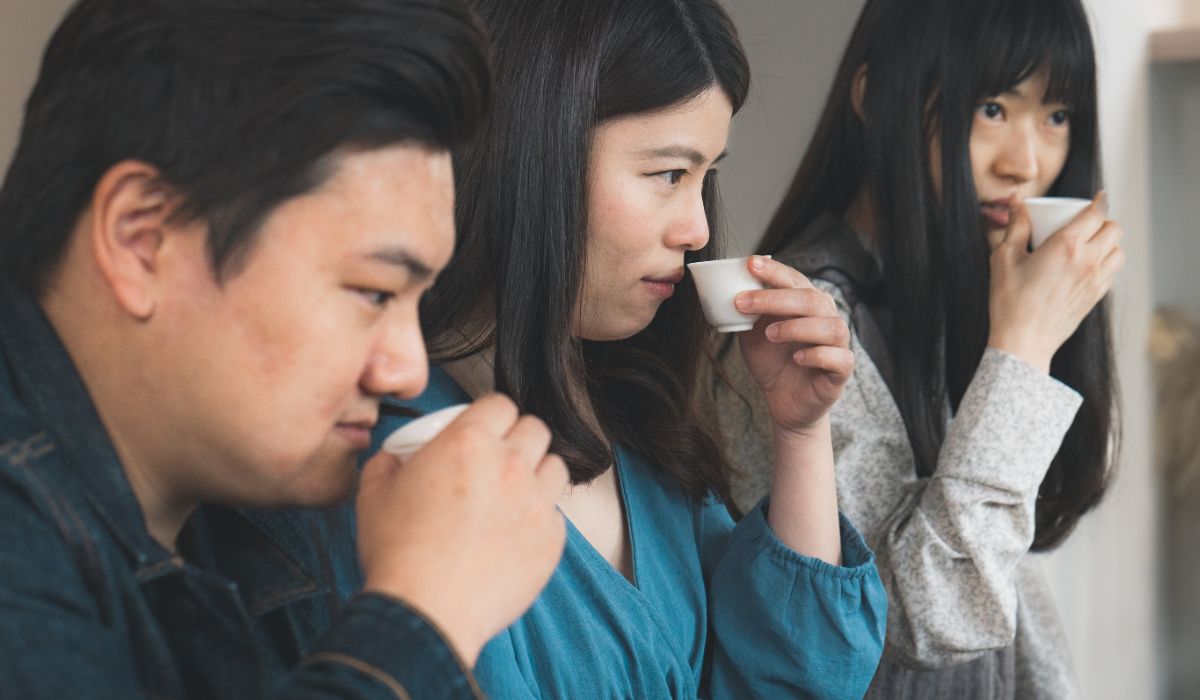

💡 Au Japon, la cérémonie traditionnelle du thé, connue sous le nom de Chanoyu, ou Sado, est un rituel chorégraphié de préparation et de service du thé vert japonais, plus précisément du matcha, axé sur l'esthétique et l'harmonie.
Achats et durabilité
Lorsque vous achetez le meilleur thé vert en feuilles, savoir d’où et comment provient votre thé peut faire toute la différence en termes de qualité et d’impact.
-
Certifications équitables et biologiques : Recherchez des thés certifiés biologiques et équitables. Ces labels garantissent que votre thé est cultivé sans pesticides ni produits chimiques nocifs et garantissent que les agriculteurs et les travailleurs impliqués sont traités et rémunérés équitablement. Cet engagement envers des pratiques éthiques contribue à une planète plus saine et à une industrie du thé plus durable.
-
Livraison gratuite et évaluations des clients : De nombreux fournisseurs de thé réputés offrent la livraison gratuite sur leurs produits, ce qui rend l'exploration d'un inventaire diversifié de thés en vrac plus facile et plus abordable. De plus, prêter attention aux notes et aux avis des clients peut vous guider vers les meilleurs thés, évalués par d’autres amateurs de thé. Ces retours peuvent être inestimables pour trouver des thés d’une qualité et d’une saveur exceptionnelles.
-
Inventaire diversifié de thés en vrac : Un bon fournisseur de thé proposera une large gamme de thés, des classiques classiques aux variétés rares et uniques. Cette diversité permet aux amateurs de thé d'explorer de nouvelles saveurs et de trouver des thés qui correspondent à leurs préférences. Que vous recherchiez les notes herbacées d'un Sencha, l'arôme sucré d'un Dragon Well ou le riche umami du Gyokuro, un inventaire diversifié vous garantit de trouver le thé parfait pour toute occasion.
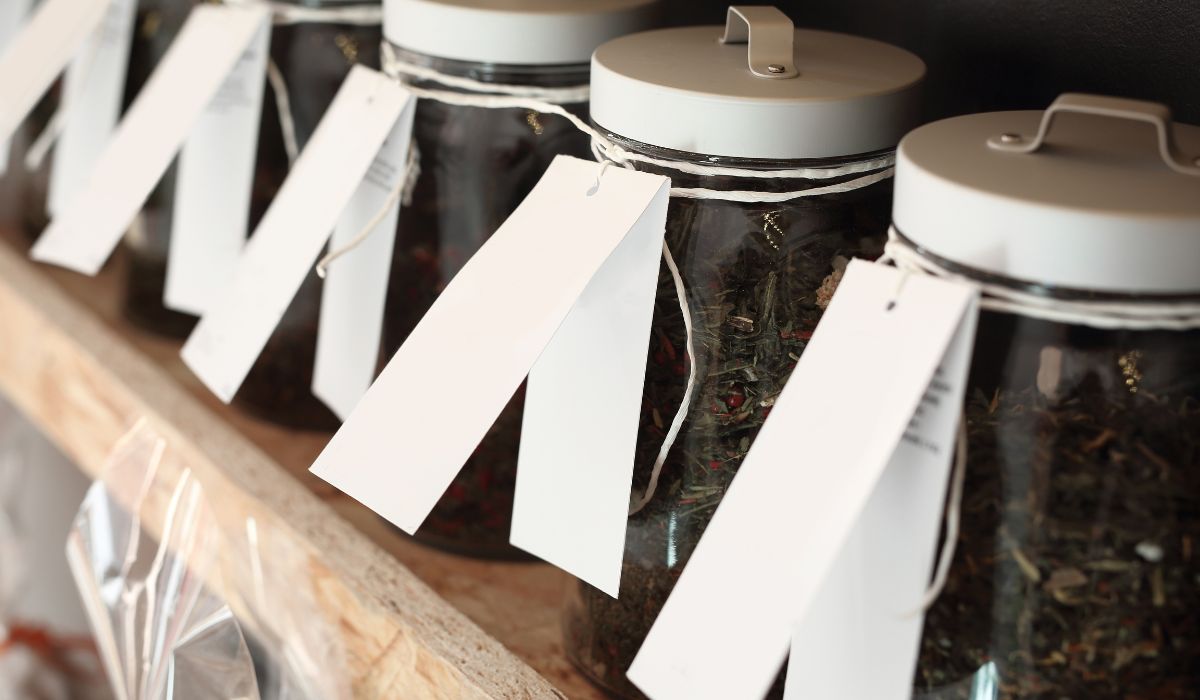

💡 La certification du commerce équitable soutient les pratiques agricoles durables et investit dans le développement communautaire, garantissant ainsi que les producteurs de thé peuvent construire un avenir meilleur pour eux-mêmes et leurs familles.
Conclusion : embrasser le monde du thé vert
Alors que nous terminons notre exploration du meilleur thé vert en feuilles, nous reconnaissons la profondeur et la diversité qu'offre cette boisson ancienne. De ses bienfaits pour la santé et de son importance culturelle au talent artistique derrière chaque variété, le thé vert se distingue comme une boisson de choix pour de nombreuses personnes dans le monde. Parmi les thés les plus raffinés se trouve le matcha Uji biologique , un produit qui incarne le summum de la qualité et de la tradition du thé vert.
Matcha Uji biologique : Cultivé dans les champs de thé vénérés d'Uji, au Japon, ce matcha n'est pas seulement un thé ; c'est un héritage culturel. Le soin méticuleux apporté à la culture et à la transformation, dans le respect de normes biologiques strictes, garantit que chaque tasse offre la saveur riche, douce et pleine d'umami qui fait la renommée du matcha. En choisissant le matcha Uji biologique, vous vous offrez une expérience de thé haut de gamme et soutenez l'agriculture durable et les pratiques agricoles éthiques.
Que vous soyez un amateur de thé chevronné ou un nouveau venu désireux d'explorer, intégrer le matcha Uji biologique à votre routine est une étape vers un mode de vie plus sain et plus conscient . Sa polyvalence, qu'il soit traditionnellement fouetté dans un bol ou comme ingrédient dans des lattés et des smoothies, en fait un parfait ambassadeur du thé vert.
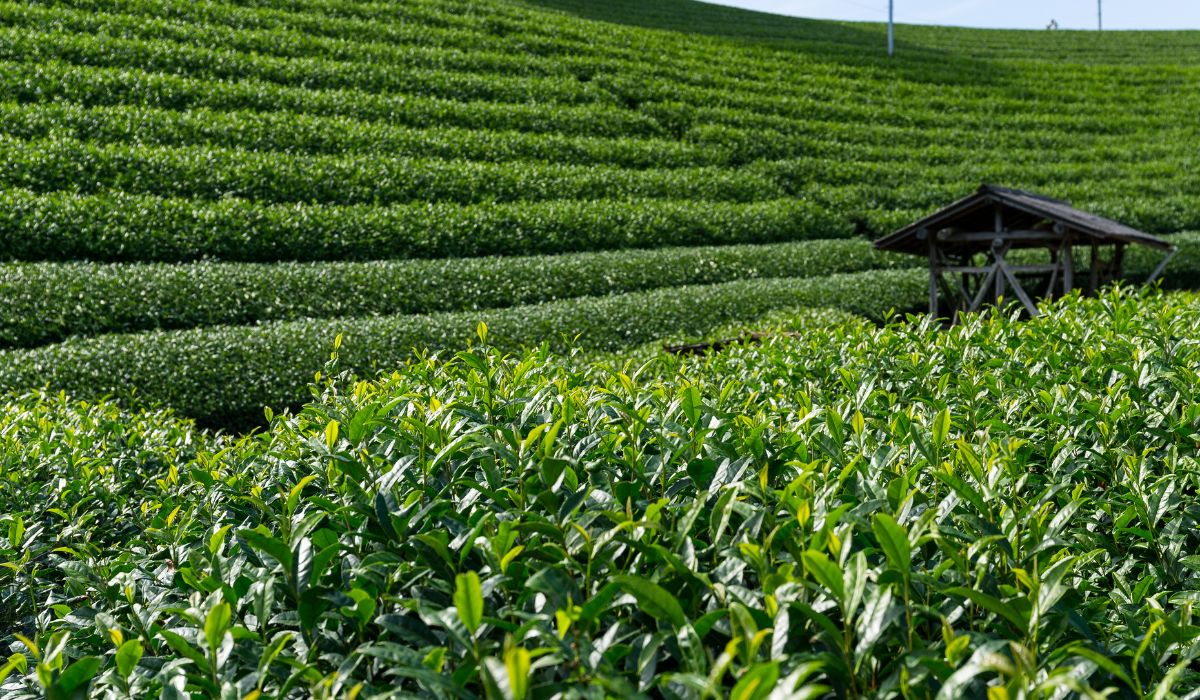

💡 Uji, une région de Kyoto, au Japon, est réputée pour produire du matcha de la plus haute qualité grâce à son climat optimal, son sol riche et ses techniques de culture du thé séculaires.
Caféine dans le thé vert Matcha : ce que vous devez savoir
Explorez le monde fascinant du thé vert matcha à travers cet article informatif. Découvrez son histoire unique, son processus d'ombrage et ses avantages pour la santé. Obtenez une compréhension complète...

Introduction
Le thé vert Matcha est une boisson populaire et saine consommée au Japon et dans d’autres régions du monde depuis des siècles. Les feuilles de thé vert sont moulues en une fine poudre et fouettées dans de l'eau chaude pour créer une boisson mousseuse et rafraîchissante. Le matcha est connu pour sa saveur unique, sa couleur verte vibrante et ses nombreux bienfaits pour la santé, notamment sa forte concentration d'antioxydants et d'acides aminés.
Comprendre le matcha et ses racines
La plante Camellia Sinensis
Le théier, Camellia sinensis , est un arbuste à feuilles persistantes originaire de Chine et d'Asie du Sud-Est. C'est la source de tous les vrais thés, y compris le thé vert, noir et blanc. Le théier est cultivé dans différents climats et conditions de sol. Pourtant, il prospère dans des températures modérées, une humidité élevée et un sol bien drainé.

Types de thé vert : un aperçu
Le thé vert est connu pour ses bienfaits pour la santé et son goût unique. Il existe différents types de thé vert, dont le sencha, le gyokuro, le hojicha et, bien sûr, le matcha, chacun ayant des caractéristiques uniques.
- Le Sencha est un thé vert délicat et rafraîchissant fabriqué à partir de feuilles de thé de haute qualité cuites à la vapeur, roulées et séchées pour produire un goût doux et doux.
- Le Gyokuro est un thé vert japonais de haute qualité cultivé à l'ombre, ce qui lui confère un goût sucré et moins amer que les autres thés verts.
- Le Hojicha est un thé vert japonais torréfié sur du charbon de bois, ce qui lui confère une saveur de noisette et de fumée.
- Le matcha est fabriqué à partir de feuilles de thé vert finement moulues et est connu pour sa couleur verte vibrante, sa saveur terreuse et ses nombreux bienfaits pour la santé.
Tous les types de thé vert regorgent d’antioxydants et sont considérés comme une boisson saine.
Ombrage ou exposition au soleil sur les plants de thé
Le thé vert ordinaire, comme le sencha et le bancha, est généralement cultivé en plein soleil . Les plantes sont généralement cultivées dans de vastes champs et exposées à un soleil abondant, ce qui permet aux feuilles de thé de se développer et de produire une saveur robuste.
Cependant, le matcha et le gyokuro sont différents. Les plants de thé sont ombragés jusqu'à un mois avant la récolte pour produire ces variétés de thé vert. Ce processus d'ombrage, connu sous le nom de « tana », consiste à recouvrir les plants de thé d'un tissu ou d'un filet, ce qui réduit la quantité de lumière solaire qui atteint les feuilles.
La restriction de l'exposition au soleil fait que les feuilles de thé deviennent plus grosses et plus fines . Il modifie également la saveur et la texture des feuilles de thé, les rendant plus sucrées, plus douces et plus délicates. L'ombrage augmente également les niveaux de chlorophylle et d'acides aminés dans les feuilles, ce qui donne une couleur verte plus brillante et une saveur umami plus intense.

Thé vert en poudre vs Matcha
La poudre de thé vert et le matcha sont souvent confondus, mais il existe une différence essentielle entre les deux. La poudre de thé vert est obtenue en broyant des feuilles de thé vert en poudre fine. Le thé vert est cultivé sous la lumière directe du soleil pendant toute la durée de sa culture. L'exposition au soleil permet aux feuilles de thé d'augmenter leurs catéchines, ou antioxydants, ce qui donne au thé vert sa saveur nettement amère .
Le matcha, une forme de poudre de thé vert, est fabriqué à partir de feuilles de thé protégées du soleil pendant plusieurs semaines avant la récolte. La restriction de la lumière du soleil augmente le niveau d'acide aminé L-théanine dans les feuilles de thé, donnant au matcha son umami distinctif. parfum et saveur. Il réduit également l’amertume et augmente les niveaux de chlorophylle, entre autres composés bénéfiques.
Ces méthodes de production uniques confèrent au matcha sa couleur verte caractéristique et sa saveur plus riche que la poudre de thé vert. De plus, le matcha est traditionnellement utilisé dans les cérémonies du thé japonaises, tandis que la poudre de thé vert est plus couramment utilisée dans la cuisine et la pâtisserie.
Sachets de thé ou poudre de thé vert
Les sachets de thé et la poudre de thé vert sont deux façons populaires de déguster le thé vert. Les sachets de thé sont pratiques et faciles à utiliser, mais contiennent souvent des feuilles de thé de moindre qualité qui ont été broyées en petits fragments. La poudre de thé vert est créée en broyant des feuilles de thé entières en une poudre fine, ce qui donne une saveur plus complexe et une concentration plus élevée de composés bénéfiques.
Bienfaits du Matcha et du Thé Vert

Santé cardiaque et antioxydants puissants dans le matcha
Le matcha contient de fortes concentrations d'antioxydants puissants bénéfiques pour la santé cardiaque . Ces antioxydants, dont le gallate d’épigallocatéchine (EGCG), peuvent aider à réduire l’inflammation et à abaisser le taux de cholestérol, réduisant ainsi le risque de maladie cardiaque.
De plus, le matcha est riche en catéchines, qui améliorent la circulation sanguine et abaissent la tension artérielle . L’intégration du matcha dans votre alimentation permet de fournir facilement à votre corps ces bienfaits pour la santé cardiaque.
Perte de poids et glycémie : l’effet du thé vert
Des études ont montré que le thé vert peut avoir un impact positif sur la gestion du poids et la régulation de la glycémie . Les composés actifs du thé vert, en particulier les catéchines, peuvent contribuer à augmenter le métabolisme et à réduire la graisse corporelle.
Le thé vert peut également améliorer la sensibilité à l’insuline et réduire l’absorption du glucose, abaissant ainsi le taux de sucre dans le sang. Ces résultats suggèrent que l’incorporation du thé vert dans une alimentation saine et une routine d’exercice favorise la perte de poids et le contrôle de la glycémie.
Vitamine C et soutien immunitaire dans le Matcha
Le matcha est une excellente source de vitamine C, un antioxydant important qui peut aider à renforcer le système immunitaire . La vitamine C est essentielle à la production de collagène. Cette protéine est vitale pour la santé de la peau, des os et des tissus conjonctifs. Il contribue également à augmenter la capacité du corps à absorber le fer, essentiel à la santé des cellules sanguines.

Équilibrer la caféine avec la L-théanine pour améliorer la fonction cognitive
Le matcha est également riche en acide aminé L-théanine, qui favorise la relaxation et réduit le stress . Cet acide aminé agit en synergie avec la caféine pour favoriser un état de vigilance calme, ce qui peut améliorer la fonction cognitive et la clarté mentale. La L-théanine améliore également la qualité du sommeil et réduit les symptômes d'anxiété et de dépression.
Teneur en caféine et son impact
Teneur en caféine du matcha par rapport au thé vert ordinaire
Le Matcha est un type de thé vert connu pour sa forte teneur en caféine. Il contient entre 18,9 et 44,4 milligrammes de caféine par gramme de poudre de matcha , soit plus que la plupart des autres types de thé vert. Cependant, la caféine du matcha est libérée plus lentement dans la circulation sanguine que la caféine du café ou des boissons énergisantes, ce qui peut conduire à un regain d'énergie plus soutenu et plus équilibré .
Comparaison des niveaux de caféine : matcha, grains de café et boissons énergisantes
Le matcha contient moins de caféine que les grains de café, qui contiennent entre 10,0 et 12,0 mg de caféine par gramme de grains . Cependant, la caféine du matcha est plus biodisponible que le café , le corps l'absorbe donc plus rapidement et plus efficacement. D’un autre côté, les boissons énergisantes peuvent contenir jusqu’à 300 mg de caféine par portion, une teneur en caféine nettement plus élevée que le matcha ou le café.

Effets de la caféine sur le système nerveux central
La caféine est un stimulant du système nerveux central qui peut améliorer la fonction cognitive, augmenter la vigilance et réduire la fatigue. Il agit en bloquant l'action de l'adénosine, un neurotransmetteur qui favorise le sommeil et la relaxation. Cependant, la caféine peut également provoquer des effets secondaires tels que nervosité, nervosité et insomnie, surtout lorsqu'elle est consommée en grande quantité.
Tension artérielle et caféine : la connexion Matcha
La caféine peut augmenter la tension artérielle chez certaines personnes, en particulier celles souffrant d'hypertension ou de maladies cardiovasculaires. Cependant, l’effet de la caféine sur la tension artérielle peut varier en fonction de l’individu et de la quantité consommée. Comme les autres thés verts, le matcha contient des composés qui abaissent la tension artérielle , ce qui peut aider à contrecarrer les effets de la caféine.
Le matcha dans la vie quotidienne
Intégrer le Matcha à votre routine quotidienne pour une santé optimale
L'intégration du matcha et du thé vert dans votre routine quotidienne peut avoir de nombreux avantages pour la santé. Essayez de consommer au moins une tasse de thé vert ou de matcha par jour pour profiter de ses bienfaits pour la santé, mais faites attention à votre consommation de caféine, surtout si vous y êtes sensible. Bien que le thé vert et le matcha soient des boissons saines, ils ne doivent pas être considérés comme une panacée pour les problèmes de santé. Une alimentation équilibrée, une activité physique régulière et des choix de vie sains restent les fondements d’une bonne santé.
Qualités inférieures de Matcha : Comprendre les différences
Le matcha est disponible en différentes qualités, chacune avec sa saveur, sa texture et son prix uniques. Les plus hautes qualités de matcha sont fabriquées à partir des feuilles de thé les plus jeunes et les plus délicates, récoltées dans des cultures de thé ombragées et moulues en une poudre fine. Les qualités inférieures de matcha sont fabriquées à partir de feuilles de thé plus anciennes et plus grossières, moins chères mais moins savoureuses et nutritives.
Matcha contre café

Le matcha est-il meilleur que le café contre l’anxiété ?
Il a été démontré que la forte concentration de L-théanine du Matcha a un effet calmant sur le corps et l'esprit. Cet acide aminé agit en synergie avec la caféine pour favoriser un état de vigilance calme , ce qui peut aider à réduire les symptômes d'anxiété et de stress. Le café, en revanche, peut augmenter l’anxiété et la nervosité chez certaines personnes, surtout lorsqu’il est consommé en grande quantité.
Matcha contre café : une confrontation avec la caféine
Le matcha contient moins de caféine que le café, mais il contient également d'autres composés qui peuvent renforcer les effets de la caféine et favoriser des niveaux d'énergie plus soutenus et équilibrés. La caféine contenue dans le café est absorbée plus rapidement et plus efficacement par le corps, ce qui entraîne une augmentation plus intense de la caféine, suivie d'une chute de caféine.
FAQ :
1. Le thé Matcha est-il riche en caféine ?
Oui, la teneur en caféine du matcha est élevée. Il contient entre 18,9 et 44,4 mg de caféine par gramme de thé , soit plus que la plupart des autres types de thé vert.
2. Le matcha est-il plus fort que le café ?
Non, le matcha n’est pas plus fort que le café en termes de teneur en caféine. Cependant, la caféine du matcha est plus biodisponible que le café, de sorte que le corps l'absorbe plus rapidement et plus efficacement.
3. Quelle quantité de caféine contient le thé vert par rapport au café ?
Le thé vert contient moins de caféine que le café, mais il contient également d'autres composés qui peuvent renforcer les effets de la caféine et favoriser un regain d'énergie plus soutenu et équilibré.
4. Le matcha est-il meilleur que le café contre l’anxiété ?
La forte concentration de L-théanine du Matcha a un effet calmant sur le corps et l'esprit. Le café, en revanche, peut augmenter l’anxiété et la nervosité chez certaines personnes, surtout lorsqu’il est consommé en grande quantité.
5. Quelle quantité de matcha est sûre par jour ?
La plupart des experts recommandent de ne pas consommer plus de 2 à 3 tasses de matcha par jour, soit environ 200 à 300 mg de caféine.
6. Le Matcha me tiendra-t-il éveillé ?
Comme d’autres sources de caféine, le matcha peut aider à favoriser la vigilance et à réduire la fatigue. Cependant, consommer trop de caféine peut également provoquer des effets secondaires tels que nervosité, nervosité et insomnie. Consommer du matcha avec modération et faire attention à sa consommation de caféine est essentiel.

Conclusion
Le thé vert Matcha est une boisson saine et délicieuse appréciée depuis des siècles. Il est riche en antioxydants, catéchines et autres composés bénéfiques qui peuvent favoriser la santé et le bien-être.
Le matcha contient également de la caféine, qui peut aider à favoriser la vigilance et à réduire la fatigue. Il est important de consommer du matcha avec modération et de faire attention à sa consommation de caféine. Avec sa saveur unique, sa couleur verte vibrante et ses nombreux bienfaits pour la santé, le matcha est une boisson que tout le monde devrait essayer au moins une fois.
Meilleur thé vert japonais : Matcha, Sencha et au-delà
Explorez le monde captivant du thé vert japonais, où les coutumes anciennes se conjuguent avec la santé et le goût. Découvrez les types distincts comme le Matcha, le Sencha et...

Introduction au thé vert japonais
Le thé vert japonais, bien plus qu’une simple boisson, fait partie intégrante de la culture japonaise. Vénéré pour sa riche histoire s'étendant sur des siècles et son rôle essentiel dans les célèbres cérémonies du thé japonaises, le thé vert au Japon symbolise l'hospitalité, la pleine conscience et l'art.
Bienfaits pour la santé du thé vert japonais
Riche en antioxydants : le thé vert japonais est un concentré d'antioxydants, en particulier de catéchines, qui combattent les radicaux libres et soutiennent la santé globale.
Stimule la fonction cérébrale : Le thé vert contient de la L-théanine, qui est liée à l'amélioration de la fonction cognitive. Cet acide aminé favorise la relaxation et la vigilance.
Allié perte de poids : Le thé vert accélère le métabolisme, contribuant ainsi à la perte et au maintien du poids.
Santé cardiaque : il est connu pour améliorer la circulation sanguine et abaisser le taux de cholestérol.
💡Le saviez-vous ? La cuisson à la vapeur des feuilles de thé vert, méthode de production utilisée au Japon, aide à conserver la couleur verte éclatante et le riche profil nutritionnel du thé.
Explorer les variétés : des sachets de thé aux feuilles mobiles
Concernant le thé, deux méthodes standards sont généralement utilisées pour sa préparation : les sachets de thé et le thé en feuilles .
- Les sachets de thé sont parfaits pour ceux qui recherchent la commodité et une préparation rapide. Ils sont faciles à utiliser et se trouvent dans presque tous les supermarchés.
- D’un autre côté, le thé en feuilles offre une expérience plus authentique, permettant à toute la saveur et l’arôme de se déployer. Le thé en feuilles est généralement de meilleure qualité et se décline en différentes saveurs. Même si la préparation demande plus de temps et d’efforts, le résultat en vaut la peine.
En fin de compte, le choix entre les sachets de thé et le thé en feuilles dépend de vos préférences personnelles et de l’occasion.
Poudre de Matcha : le cœur du thé japonais
Le matcha est la poudre finement moulue de feuilles de thé vert spécialement cultivées et transformées, et il est considéré comme le summum du thé vert japonais. Il est célèbre pour ses couleurs vives, son goût riche et sa polyvalence dans les cérémonies traditionnelles et les utilisations culinaires modernes.
Dans la cérémonie traditionnelle du thé japonaise, le matcha est considéré comme un symbole d’hospitalité et de savoir-faire. D’autre part, dans les utilisations culinaires modernes, le matcha ajoute une saveur unique à divers plats allant des lattés aux desserts.
Le matcha est un superaliment riche en antioxydants qui aident à stimuler le métabolisme et à améliorer la santé globale.
Camellia Sinensis : La source
Le théier Camellia Sinensis produit toutes sortes de thé vert, y compris ceux du Japon. En raison de ses techniques de culture et de transformation spécifiques, il entraîne des variations de saveur, d’arôme et de couleur.
La plante est utilisée pour la production de thé et est très appréciée pour ses propriétés médicinales. Camellia Sinensis joue un rôle important dans la culture humaine depuis des siècles, ce qui en fait une plante intéressante et fascinante.
Thé Gyokuro : une expérience premium
Si vous êtes amateur de thés de haute qualité, essayez Gyokuro. C'est un thé vert japonais de première qualité qui possède un profil aromatique unique. L’une des choses qui distingue le Gyokuro des autres thés verts est sa saveur umami exceptionnelle. Ceci est accompli en ombrageant les plants de thé pendant plusieurs semaines avant de récolter les feuilles.
Ce processus améliore la concentration de L-théanine et de caféine dans les feuilles de thé, ce qui donne un goût sucré et moelleux incroyablement satisfaisant. Le Gyokuro est un thé qui se déguste lentement, permettant d'apprécier pleinement sa saveur complexe et nuancée. Si vous recherchez une expérience de thé vraiment haut de gamme, alors Gyokuro vaut la peine d'être essayé.
💡 Gyokuro signifie « rosée précieuse » en japonais. Ce nom reflète son statut estimé et l’aspect rosée de son infusion.
Thé Bancha : le thé vert japonais de tous les jours
Le thé Bancha, également connu sous le nom de « thé commun » ou « thé grossier », est un thé vert japonais récolté à partir de la deuxième récolte de feuilles de thé. Il est connu pour sa saveur douce et moelleuse, avec une nuance légèrement noisetée et terreuse.
Le thé Bancha est également faible en caféine, ce qui en fait un excellent choix pour ceux qui souhaitent savourer une tasse de thé sans nervosité. En raison de sa saveur douce, il est souvent consommé comme thé de tous les jours au Japon. C'est un choix populaire parmi les amateurs de thé du monde entier. Donc, si vous n’avez pas encore essayé le thé Bancha, cela vaut la peine d’être exploré !
Thé Bio : Un Délice Pur et Naturel
Le thé vert japonais biologique fait le bonheur des amateurs de thé qui apprécient la pureté et le goût naturel de leurs infusions. Contrairement aux thés conventionnels, le thé biologique est cultivé sans engrais ni pesticides synthétiques, ce qui en fait un choix plus sain et plus sûr pour vous et pour l'environnement.
Non seulement le thé biologique offre un goût délicieux, mais il constitue également un engagement en faveur de la durabilité environnementale et de la santé. En choisissant du thé biologique, vous soutenez les agriculteurs qui utilisent des pratiques agricoles respectueuses de l'environnement qui contribuent à préserver l'équilibre délicat de la nature.
Le thé biologique est donc la solution idéale, que vous recherchiez une tasse de thé rafraîchissante ou une boisson plus saine. Profitez du goût pur et naturel du thé vert japonais biologique et faites un pas vers un avenir plus sain et plus durable.
Thé de haute qualité de la préfecture de Kagoshima
Essayez le thé vert japonais de haute qualité de la préfecture de Kagoshima si vous aimez le thé. Ce thé est réputé pour son arôme, sa saveur et sa couleur exceptionnels, qui résultent de divers facteurs tels que la première récolte, la région où il est cultivé et les méthodes de transformation méticuleuses utilisées par des artisans qualifiés.
Grâce à ses conditions climatiques favorables et à son sol fertile, Kagoshima produit des feuilles de thé de la plus haute qualité. La région est située à la pointe sud de l’île de Kyushu. Elle est réputée pour son thé vert exceptionnel, réputé pour sa douceur délicate et son riche goût umami.
La transformation des feuilles de thé est un art dans la préfecture de Kagoshima. Les artisans utilisent des méthodes traditionnelles et accordent une attention particulière à chaque détail pour garantir que la saveur et l'arôme du thé ne soient pas compromis. Le thé est soigneusement récolté, cuit à la vapeur et séché pour préserver sa fraîcheur et sa qualité.
Alors, pour découvrir le goût riche et authentique du thé vert japonais, mettez la main sur du thé de haute qualité de la préfecture de Kagoshima.
Thé vert chinois vs thé vert japonais
Le thé vert est une boisson incroyablement populaire dans le monde entier, et deux des variétés les plus connues sont le chinois et le japonais. Bien que les deux types de thé proviennent de la même plante Camellia sinensis, ils diffèrent par leurs méthodes de transformation, ce qui conduit à des saveurs et des arômes uniques.
Le thé vert chinois est généralement cuit à la poêle, ce qui aide à arrêter l'oxydation et à préserver les saveurs naturelles. Cette méthode donne au thé une saveur de noisette torréfiée et un arôme légèrement fumé. Certains thés verts chinois célèbres incluent le thé Dragonwell (Longjing) et le thé Gunpowder (Zhu Cha).
En revanche, le thé vert japonais est cuit à la vapeur, ce qui permet aux feuilles de conserver une couleur et une saveur plus naturelles. Il en résulte un goût plus frais et herbacé avec un arôme végétal. Le Sencha et le Matcha sont deux des types de thé vert japonais les plus populaires.
Ainsi, en fonction de vos préférences gustatives, vous pourrez choisir entre ces deux types de thé vert et profiter de leurs saveurs et bienfaits uniques.
Thé vert ordinaire ou thé cultivé à l'ombre
L’une des principales différences entre les variétés de thé vert est de savoir si elles sont cultivées en plein soleil ou à l’ombre. Le thé vert ordinaire est cultivé en plein soleil, ce qui amène les feuilles de thé à produire plus de tanins, ce qui lui donne un goût plus astringent et amer.
D’un autre côté, les thés cultivés à l’ombre comme le Gyokuro et le Matcha sont protégés de la lumière directe du soleil, ce qui augmente leur teneur en chlorophylle et leur donne une saveur plus douce et plus riche en umami. En plus de leur goût, les thés cultivés à l’ombre sont également connus pour leur couleur verte vibrante et leurs niveaux plus élevés d’antioxydants et d’autres composés bénéfiques.
Donc, si vous recherchez une tasse de thé plus douce et plus savoureuse, essayez les thés verts cultivés à l’ombre.
Thé noir : un autre type d'infusion
Lorsqu’il s’agit de thé, la plupart des gens considèrent le thé vert comme la boisson japonaise par excellence. Cependant, un autre type de thé qui gagne en popularité au Japon est le thé noir, également connu sous le nom de « Wakocha ».
Wakocha est un thé entièrement oxydé avec un profil aromatique unique par rapport aux autres thés japonais. Son goût est plus fort et sa teneur en caféine est plus élevée, ce qui en fait un excellent choix pour ceux qui veulent un peu plus de piquant dans leur tasse de thé.
Ce qui est intéressant avec le Wakocha, c'est que ce n'est pas un thé japonais traditionnel. Les Britanniques l’ont introduit à la fin du 19e siècle et il est depuis devenu une alternative populaire au thé vert. Bien qu'il ne soit peut-être pas aussi connu que le thé vert, le Wakocha vaut la peine d'être essayé pour tous ceux qui aiment un thé audacieux et savoureux.
💡 Le Wakocha est un ajout relativement nouveau au répertoire du thé japonais, gagnant en popularité pour sa saveur douce et sucrée, distincte des thés noirs traditionnels.
Thé vert pour perdre du poids
Le thé vert japonais, en particulier les variétés comme le Sencha, est une boisson saine et largement consommée, très appréciée pour ses nombreux bienfaits pour la santé. L’un des avantages les plus notables du thé vert japonais est sa capacité à contribuer à la perte de poids. Cela est dû à la présence de catéchines, un antioxydant présent dans le thé vert.
Les catéchines sont connues pour accélérer le métabolisme et augmenter la vitesse de combustion des graisses par le corps. Cela peut entraîner une réduction du poids corporel et du pourcentage de graisse corporelle. Le thé vert japonais est également connu pour contenir de la caféine, qui peut stimuler davantage le métabolisme et augmenter les niveaux d'énergie, ce qui en fait une excellente alternative aux boissons sucrées et riches en calories.
L'intégration du thé vert japonais dans votre routine quotidienne peut être un moyen efficace et sain de contribuer à la perte de poids et d'améliorer la santé globale.
Thé Sencha : le choix populaire
Le thé vert Sencha est un thé tendance et très consommé au Japon. Réputé pour son équilibre parfait entre douceur et astringence, le thé Sencha offre un délicieux profil aromatique qui peut être dégusté aussi bien chaud que froid.
Le thé Sencha contient des niveaux élevés d’antioxydants, ce qui en fait un excellent choix pour une boisson saine et rajeunissante pour les amateurs de thé. Sa saveur et son arôme uniques en font un complément parfait à divers aliments, ce qui en fait une boisson idéale à accompagner des repas.
La popularité du thé Sencha peut être attribuée à sa riche histoire et à son importance culturelle au Japon. Le thé est fabriqué à partir des feuilles supérieures de la plante Camellia sinensis. Il est généralement cuit à la vapeur et roulé pour préserver sa saveur et son arôme délicats.
Dans l’ensemble, le thé Sencha est un excellent choix pour ceux qui recherchent un thé sain, savoureux et culturellement significatif qui peut être dégusté à tout moment.
Préfecture de Shizuoka : le cœur du thé japonais
La préfecture de Shizuoka, au centre du Japon, est célèbre pour sa production de thé de haute qualité. Le climat idéal de la région, son sol fertile et ses précipitations abondantes créent des conditions parfaites pour la culture du thé, ce qui donne lieu à certains des thés les plus savoureux et aromatiques du Japon. Shizuoka est particulièrement célèbre pour produire du sencha, un thé vert rafraîchissant au goût herbacé avec une touche sucrée.
La région est également connue pour son matcha de qualité supérieure, une fine poudre obtenue en broyant des feuilles de thé cultivées à l'ombre, ce qui lui confère une saveur riche et crémeuse. Si vous êtes un passionné de thé et que vous souhaitez découvrir la meilleure culture du thé japonaise, la visite de Shizuoka est un incontournable.
Fonction cérébrale et thé vert
Saviez-vous que la consommation régulière de thé vert japonais, en particulier de Matcha, est liée à une amélioration des fonctions cérébrales ? Il a été démontré que la combinaison de caféine et de L-théanine présente dans le thé vert Matcha améliore la clarté cognitive, la concentration, le temps de réaction et la mémoire.
La caféine stimule le système nerveux central, ce qui augmente la vigilance et améliore les performances cognitives. Parallèlement, la L-théanine favorise la relaxation et réduit l’anxiété. Cette combinaison unique de composés naturels fait du thé vert Matcha un moyen délicieux et sain de stimuler les fonctions cérébrales et la productivité.
Alors, la prochaine fois que vous aurez besoin d’un remontant mental, pourquoi ne pas essayer une tasse de thé vert Matcha et constater la différence que cela peut faire pour vos performances cognitives ?
Thés produits en masse vs thé vert japonais artisanal
Si vous êtes amateur de thé, vous devez avoir essayé différents types de thé. Mais avez-vous déjà essayé le thé vert japonais artisanal ? Il est considéré comme l’un des meilleurs types de thé disponibles sur le marché. Contrairement aux thés produits en masse, qui sont souvent insipides et dépourvus de bienfaits nutritionnels, les thés artisanaux sont méticuleusement élaborés par des maîtres de thé experts, offrant un profil plus riche et plus complexe qui reflète véritablement le terroir et l'expertise du maître de thé.
Le thé vert japonais artisanal n’est pas seulement une boisson mais une expérience qui ravit tous les sens. L'arôme, le goût et la texture de ces thés sont sans précédent et laissent une impression durable en bouche. Ils sont non seulement délicieux, mais regorgent également de nombreux bienfaits pour la santé. Ils sont riches en antioxydants, vitamines et minéraux qui aident à renforcer l’immunité, à réduire le stress et à favoriser le bien-être général.
Du sencha délicat au matcha corsé, les thés verts japonais artisanaux se déclinent en différentes saveurs et textures, répondant à différents goûts et préférences. Le Sencha, par exemple, est un thé léger et rafraîchissant, parfait à boire en journée. En même temps, le matcha est un thé corsé connu pour sa saveur audacieuse et sa texture crémeuse. Ainsi, que vous recherchiez une saveur subtile ou audacieuse, il existe un thé pour tous les goûts et toutes les occasions.
Supposons que vous soyez un amateur de thé qui apprécie les nuances subtiles d’une infusion bien conçue ou que vous recherchiez simplement une façon plus saine et plus délicieuse de rester hydraté. Dans ce cas, les thés verts japonais artisanaux sont un excellent choix. Alors pourquoi se contenter de moins que le meilleur ? Essayez le thé vert japonais artisanal dès aujourd'hui et embarquez pour un voyage de gourmandise et de bien-être.
Thé Oolong : une infusion japonaise différente
Vous connaissez peut-être les thés japonais populaires comme le thé vert et le matcha si vous êtes amateur de thé. Cependant, il existe un autre type de thé moins connu au Japon : le thé Oolong. Bien qu’il soit originaire de Chine, le thé Oolong a gagné en popularité dans le monde entier. Les thés Oolong japonais sont une variante unique de ce type de thé.
Le thé Oolong japonais se distingue par son profil plus léger et plus floral que son homologue chinois. En effet, il utilise un processus différent, oxydant partiellement les feuilles de thé et comblant le fossé entre les thés verts et noirs. Alors, si vous souhaitez essayer quelque chose de différent, pourquoi ne pas essayer le thé Oolong japonais ?
💡 Le thé Oolong japonais, bien que moins répandu, est de plus en plus reconnu pour ses saveurs délicates et ses bienfaits pour la santé, similaires à ceux du thé vert.
Explorer les nuances du thé vert japonais
Genmaicha, ou « thé pop-corn », est un thé vert japonais mélangé à du riz brun torréfié. Cette combinaison unique d’ingrédients offre une saveur de noisette réconfortante qui se distingue des autres types de thé.
En raison de sa faible teneur en caféine, il est populaire auprès de ceux qui souhaitent savourer une tasse de thé apaisante sans la nervosité qui peut accompagner des niveaux de caféine plus élevés. Genmaicha est un thé délicieux et satisfaisant, parfait pour toutes les occasions.
Plantes à thé : divers cultivars, diverses saveurs
Le Japon est connu pour son thé vert, qui se décline en différentes saveurs et arômes grâce aux différents cultivars utilisés dans sa production. Samidori, Saemidori, Okumidori, Gokou, Yabukita, Asahi et Kanayamidori sont parmi les cultivars les plus populaires. Chaque cultivar possède des caractéristiques uniques qui contribuent au goût général du thé.
Par exemple, le Yabukita est connu pour ses notes végétales, tandis que l'Asahi est apprécié pour sa saveur intense d'umami. Ces variétés sont soigneusement cultivées et transformées pour créer la tasse de thé parfaite, garantissant que chaque gorgée soit un délice pour les sens.
Matcha de haute qualité : une expérience luxueuse
Le matcha de qualité cérémonielle est le matcha de la meilleure qualité disponible, fabriqué à partir des feuilles de thé les plus jeunes et les plus délicates. Il est très apprécié pour sa couleur vibrante, sa saveur délicate et son utilisation traditionnelle dans les cérémonies du thé japonaises. Consommer du matcha de qualité cérémonielle est considéré comme une expérience luxueuse et parfait pour les occasions spéciales.
Le matcha de qualité cérémonielle peut être dégusté sous forme d'usucha ou de koicha (thé fin ou épais) et est fouetté avec de l'eau chaude à l'aide d'un Chasen en bambou. Il a une saveur umami intense et une astringence minimale, ce qui en fait une boisson délicieuse et saine pour les amateurs de thé.
Culture japonaise et thé vert
Le thé vert japonais est profondément enraciné dans la culture japonaise et symbolise l'hospitalité, la paix et la simplicité. Il est considéré comme un patrimoine culturel qui offre un voyage de découverte.
Il favorise le bien-être, la clarté mentale et une sensation de calme grâce à ses riches antioxydants, vitamines et acides aminés. Le thé vert japonais n’est pas seulement une boisson mais une profonde expérience spirituelle et esthétique.
Flush Sencha : le premier choix
Récoltée au printemps, la première pousse de Sencha est très appréciée pour sa saveur fraîche et vibrante. Il est considéré comme de la plus haute qualité et constitue une parfaite introduction au thé vert japonais.
La première récolte contient les niveaux les plus élevés d'antioxydants et de composés bénéfiques, car les feuilles de thé n'ont pas été cueillies depuis la saison des récoltes de l'année précédente. Après la première pousse, les plants de thé poussent de nouvelles feuilles de thé, qui sont à nouveau récoltées dans un délai d'un mois. Ce processus se reproduit pour le troisième rinçage. Certaines plantations de thé récoltent également en automne et en hiver.
Les amateurs de thé doivent comprendre les récoltes pour prendre des décisions éclairées lors de la sélection de leur thé. La première bouffée de printemps, connue sous le nom d' ichibancha en japonais, est le thé le plus concentré et le plus savoureux. Les récoltes ultérieures sont appauvries en composition nutritionnelle et en saveur. Par conséquent, il faut toujours opter pour la première récolte de printemps dans la mesure du possible.
L'importance de la cérémonie du thé japonaise
La cérémonie japonaise du thé est un élément essentiel de la culture japonaise. C'est bien plus qu'un simple acte de boire du thé. Il incarne l'harmonie, le respect, la pureté et la tranquillité, reflétant la philosophie profonde de la culture japonaise.
Le fouet en bambou, ou Chasen, est indispensable à la préparation du Matcha. Il aide à créer une texture lisse et sans grumeaux et le dessus mousseux caractéristique d’un Matcha bien préparé.
Moines bouddhistes et thé vert : un lien historique
La tradition du thé vert au Japon a commencé il y a des millénaires, sous l'influence des moines bouddhistes qui apportaient des graines de thé de Chine. La production de thé vert japonais de haute qualité nécessite une culture méticuleuse, un traitement précis et une profonde appréciation de la tradition. C'est un engagement à offrir une expérience de thé supérieure.
Brassage à l'eau froide : une touche rafraîchissante
Infuser du thé vert japonais avec de l'eau froide, en particulier du Sencha et du Gyokuro, fait ressortir une saveur plus douce et plus sucrée, ce qui en fait une alternative rafraîchissante à l'infusion chaude. L'infusion à l'eau chaude est la méthode traditionnelle, idéale pour extraire toute la gamme des goûts, notamment dans les thés comme le Sencha et le Bancha.
Trouver votre thé vert japonais préféré
Découvrir votre thé vert japonais préféré est un voyage personnel. Il s’agit d’explorer différentes variétés et méthodes de brassage pour trouver celle qui résonne avec votre palais. Investir dans du thé vert japonais haut de gamme est un investissement dans la qualité. Il s'agit de profiter des meilleures saveurs, arômes et bienfaits pour la santé.
Conclusion : embrasser le monde du thé vert japonais
Le monde des saveurs à découvrir est vaste et passionnant. Nous vous invitons à commencer votre voyage avec le thé vert japonais en explorant différentes variétés, en expérimentant des techniques de brassage et en trouvant votre préféré.
Rester en contact
Inscrivez-vous pour des offres et promotions exclusives.



















